DMSBBFAN
Overview
DMSBBFAN camera module is equipped with OmniVision CMOS image sensor OV02311 and Maxim GMSL serializer MAX96717F. It has an automotive-grade sensor with a well-tuned Image Signal Processor (ISP) that produces exceptional image quality, It is also equipped with an infrared automotive grade lens that supports 940nm infrared light recognition.
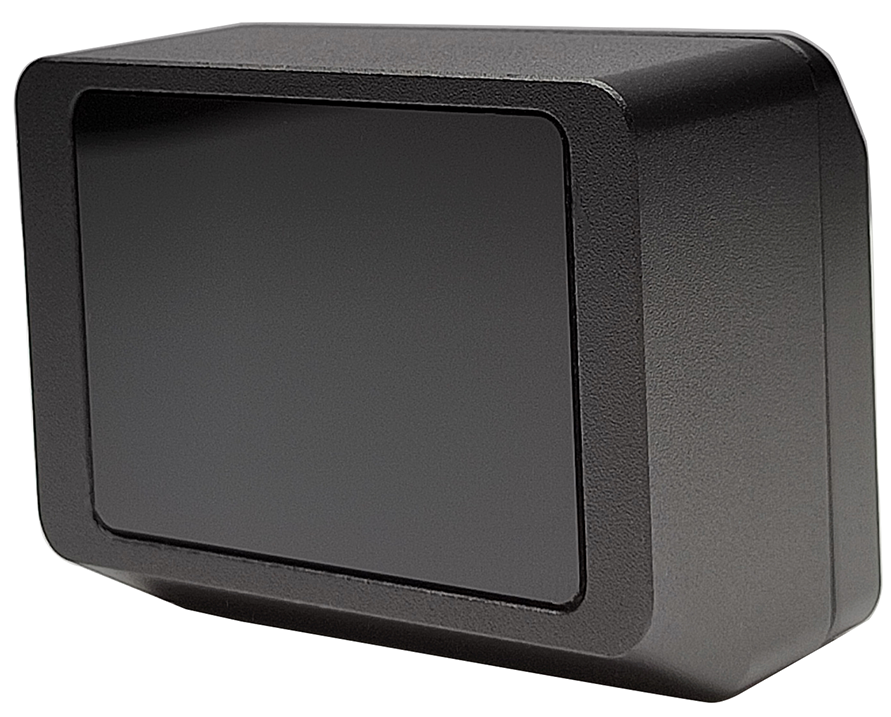

Getting Started
Specification
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Sensor | OV 2.08MP OV02311 Monochrome |
| ISP | GW5200 |
| Image Size | 1/2.9 inch CMOS |
| Output Pixels | 1600H*1300V |
| Pixel Size | 3um*3um |
| Frame Rate | 1600H*1300V@30fps |
| Output data | YUV422@8bit |
| Serializer | MAXIM MAX96717F |
| IR Filter | 940nm band pass |
| Camera Interface | GMSL2 |
| Power Supply | POC: 9~16V , LED: 9 ~16V DC |
| Current | POC: Less than 250mA@12VDC, LED: Less than 400mA@12VDC |
| Connector | Amphenol Fakra (Z Code) + Molex |
| Operating temp. range | -40~+85℃ |
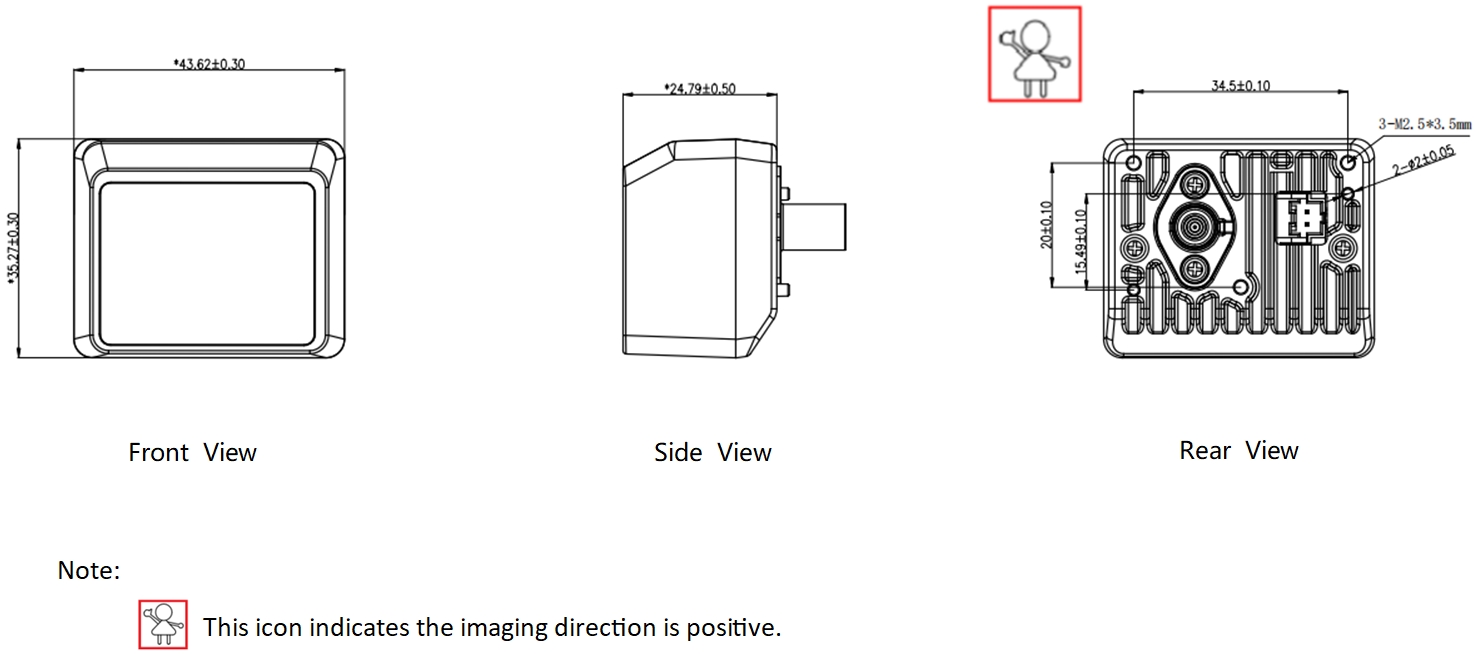
| Dimensions | W: 35.3mm, L:43.6mm, H:24.8mm |
| Weight | Less than 50g |
Dimensions
Hardware Overview
Block Diagram
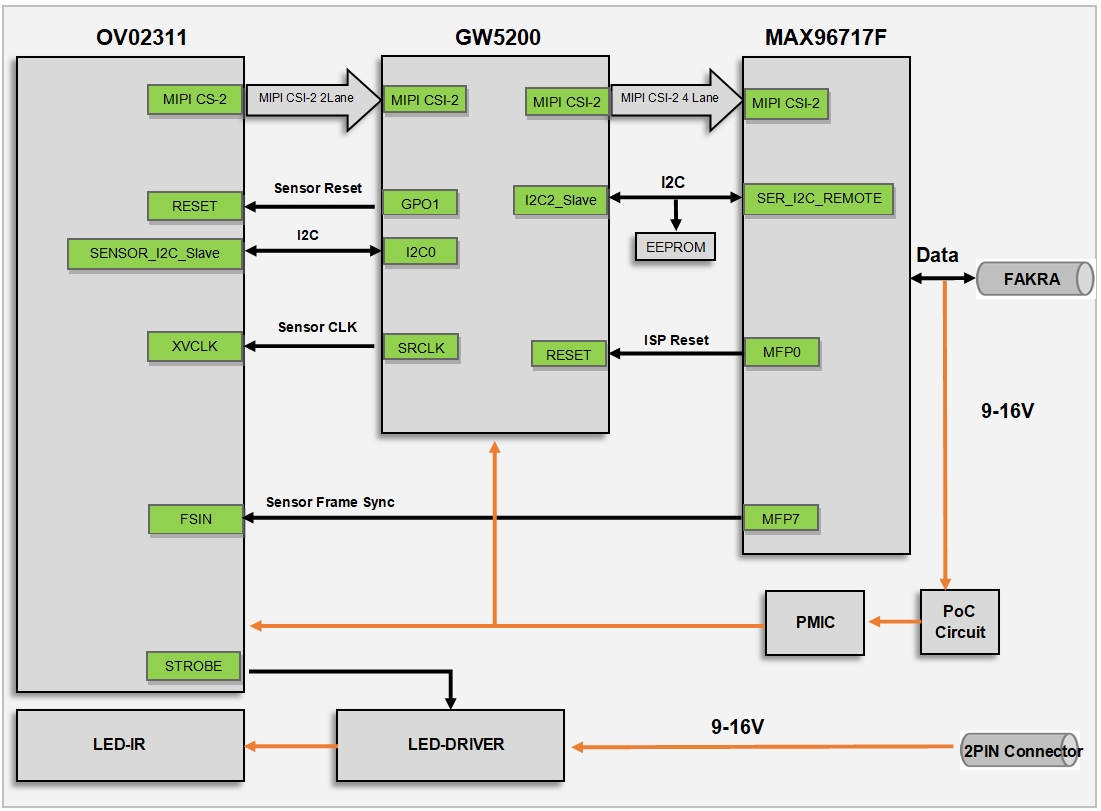
I2C Address Information
| Component | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Serializer | Model | Max96717F |
| I2C Address | 0x80 (8bit address) | |
| GMSL Rate | GMSL2 (3G bps) | |
| ISP | Model | GW5200 |
| I2C Address | 0xDA (8bit address) | |
| Reset | Controlled by Max96717F MFP0 | |
| Sensor | Model | OV02311 |
| I2C Address | 0xC0 (8bit address) | |
| Frame Sync | Controlled by Max96717F MFP7 | |
| ERROR | Controlled by Max96717F MFP3 |
LED Connector Pin Definition

| Pin Definition | Operating Voltage Range | Steady State Current | Interface Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIN | Description | Max(V) | Min(V) | (mA) | |
| 1 | VCC+ | 16 | 9 | <400mA@12V | Molex (5600200220) |
| 2 | GND | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Lens Options
| Model | HFOV | VFOV | F.No | EFL | Max Optical Distortion | Water-proof | Lens Mount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSBBFAN | 55° | 44.4° | 2.2 | 5.1mm | -0.09%@HFOV | IP5X | M9 |
Parts List
- DMSBBFAN
- Power Supply Cable
Employing Camera
1. Adaptation to NVIDIA® Jetson™ platform
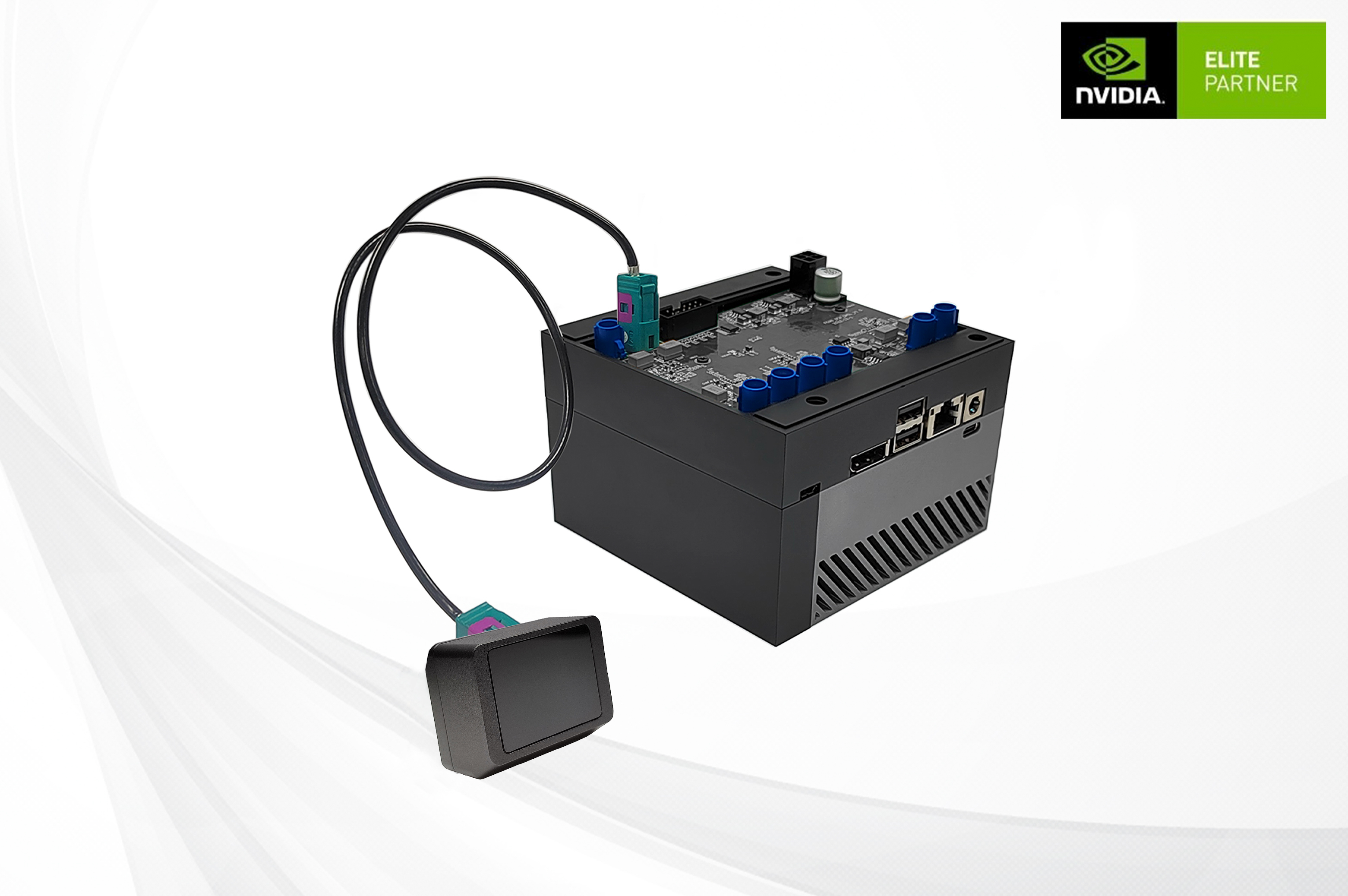

DMSBBFAN Camera Connect to Nvidia Jetson AGX Orin
Step 1: Installation Steps
- Connect the DMSBBFAN camera to the SG8A-ORIN-GMSL2 board using the coaxial cable
- Mount the SG8A-ORIN-GMSL2 board onto the Jetson AGX Orin module
- DMSBBFAN camera Connect the power supply
- SG8A-ORIN-GMSL2 board Connect the power supply
- Power on the system
Step 2: Software Preparation
-Select the appropriate driver package based on your camera type and JetPack version:
-Copy the full link address to DownGit to download
| NO. | JetPack Version | NVIDIA Jetson Devices | Adapter Board | Download Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JP5.1.2 | Jetson AGX Orin Developer Kit | SG8A-ORIN-GMSL2-F | Download |
| 2 | JP6.2 | Jetson AGX Orin Developer Kit | SG8A-ORIN-GMSL2-F | Download |
NVIDIA JetPack (Jetpack 5.1.2 or Jetpack 6.0 ) is the official software development kit (SDK) for the Jetson series of development boards. It includes the operating system, drivers, CUDA, cuDNN, TensorRT, and other development tools and libraries. Each JetPack version typically corresponds to a specific Jetson Linux version (formerly known as L4T - Linux for Tegra).
- 36.4.3: L4T R36.4.3 (Jetpack 6.2)
- 36.4: L4T R36.4 (Jetpack 6.1)
- 36.3: L4T R36.3 (Jetpack 6.0)
- 35.4.1: L4T R35.4.1 (Jetpack 5.1.2)
For more information, visit NVIDIA's official Jetson Download Center.
2. Camera Integration with Customer's Self-developed Platform
For customers with their own deserializer who want to adapt our camera (serializer) to their platform, detailed technical coordination is required.
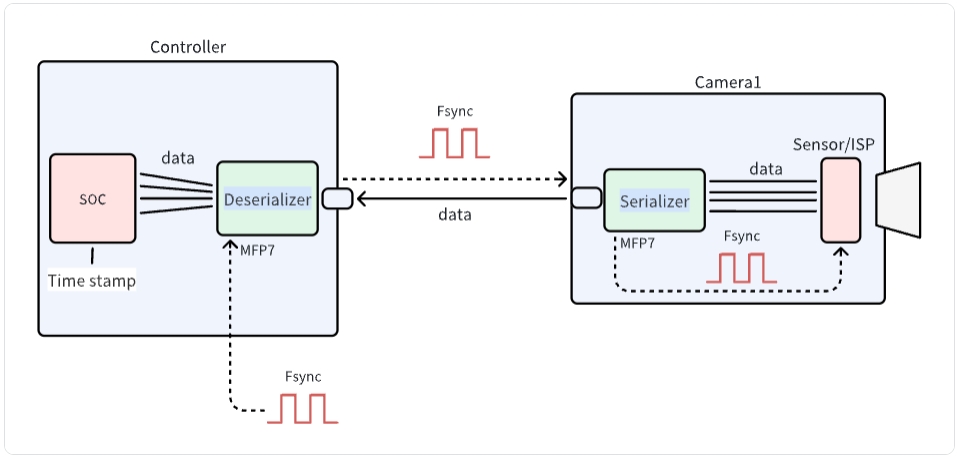
The diagram illustrates the communication architecture between a camera and controller system. It shows how data flows from the Sensor/ISP through the Serializer on the Camera side, across to the Deserializer and SOC on the Controller side. The system utilizes Fsync signals for synchronization and MFP7 interfaces for control. This architecture is essential for proper integration of SENSING cameras with customer-developed platforms.
Step 1: Link Register initialization
SENSING will provide:
-
Serializer and Deserializer Configuration
- Register configuration for the camera module-Getting Camera Information
- I2C communication protocol details
-
Link Status Troubleshooting Guide
- Link training parameters
- Error detection settings
Please refer to the software flow and demo code below to develop your driver code.
Software Development
- Driver Development:
/* Example code for MAX9296 I2C initialization */
#define MAX9296_I2C_ADDR 0x90 // 8-bit address
int max9296_init() {
// Initialize I2C bus
i2c_init();
// disable MIPI output
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0313, 0x00);
delay_ms(100);
// Configure link settings for GMSL2 (3Gbps)
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0001, 0x01);
// Configure linkA and linkB settings for GMSL2 selection (default value)
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0006, 0xC0);
// Configure MIPI rate 1200Mbps
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0320, 0x2C);
// enable MIPI output
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0313, 0x02);
return 0;
}
- Camera Configuration:
/* Example code for OMSBDAAN initialization */
#define MAX9295_I2C_ADDR 0x80 // 8-bit address
int camera_init() {
// Initialize deserializer first
max9296_init();
// Reset ISP through MAX9295A
i2c_write(0x80, 0x02BE, 0x10); // MFP0 high
//
i2c_write(0x80, 0x0057, 0x12);
i2c_write(0x80, 0x005B, 0x11);
// Configure datatype YUV422 8bit
i2c_write(0x80, 0x0318, 0x5E);
// camera trigger MFP7 low to high
i2c_write(0x80, 0x02D3, 0x00); // MFP7 low
delay_ms(300);
i2c_write(0x80, 0x02D3, 0x10); // MFP7 high
return 0;
}
Integration Steps
-
BSP Integration:
- Modify the device tree to include the CSI interface configuration
- Add camera driver to kernel build configuration
- Configure media controller pipeline for the camera
-
Application Development:
/* Example code for capturing camera frames */
#include "camera_api.h"
int main() {
// Open camera device
int fd = open("/dev/video0", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("Failed to open camera device");
return -1;
}
// Configure video capture format
struct v4l2_format fmt = {0};
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = 1600;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = 1300;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set format");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
// Request and map buffers
// ... (buffer setup code) ...
// Start streaming
// ... (streaming code) ...
// Capture and process frames
// ... (frame processing code) ...
// Cleanup
close(fd);
return 0;
}
Step 2: Data Processing
After receiving the module data through the MIPI CSI interface:
- Data Reception
- MIPI CSI-2 protocol implementation
- Data rate configuration
- Clock synchronization
- Image Processing
- Raw/YUV data parsing
- Image format conversion
- Display configuration
Technical Support
-
Documentation
- Detailed register descriptions
-
Engineering Support
- Technical consultation
- Debug assistance
- Performance optimization
SENSING Technology provides technical support for integration with most platforms. For detailed documentation, sample code, and technical assistance, please contact our support team.