Getting Started with GMSL2 Camera Splitter
Overview
The GMSL2 Camera Splitter, engineered by SZ SENSING TECH CO.,LTD., enables a single GMSL input to be distributed to two GMSL outputs while maintaining identical data streams. This device is compatible with SENSING GMSL camera models.
- Lossless data transmission
- Full GMSL/GMSL2 compatibility
- Ultra-low latency (microsecond level)
- Minimal insertion loss

Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Transport Protocol | GMSL / GMSL2 |
| Input Ports | 1 |
| Output Ports | 2 |
| Input Interface | 1× GMSL2 |
| Output Interface | 2× GMSL2 |
| Supported Data Rates | 1.5Gbps, 3Gbps, 6Gbps |
| Maximum Resolution | Up to 3840×2160 |
| Output Synchronization Accuracy | < 10μs |
| Power Supply | Yes |
| Connector | Fakra Z Type |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
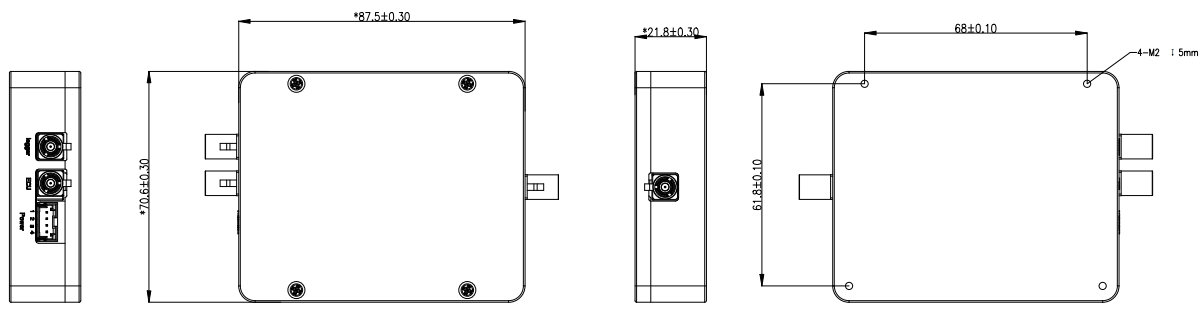
| Dimensions | 87.5mm × 70.6mm × 20mm |
| Color | Black |
| Weight | < 150g |
Dimensions
Hardware Overview
Block Diagram
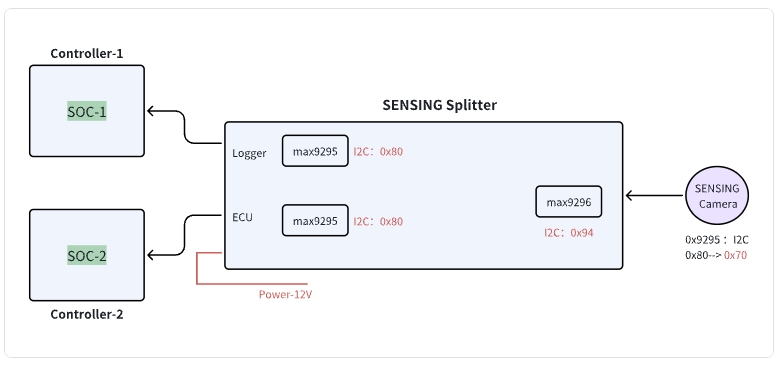
I2C Address Information
| Device | I2C Address (8-bit) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Splitter: Logger | 0x80 |
| 2 | Splitter: ECU | 0x80 |
| 3 | Splitter: Camera | 0x94 |
| 4 | SENSING Camera | 0x70 |
Connector Pin Definition
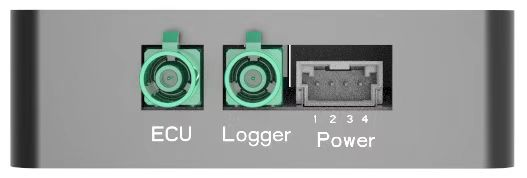
| Connector Component | Part Number | Manufacturer/Note |
|---|---|---|
| Splitter Device Connector | 50352-0400 | Molex |
| Cable Harness Connector | 50351-0400 | Molex |
| Power Supply | Pin3, Pin4 | 9~12V DC |
| Ground | Pin1, Pin2 | Common Ground |
Cable Harness Definition

Product Models
| Product Model | Input Channels | Output Channels | Resolution Support | Processor | Data Transfer Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG2-BP0102-GMSL | 1CH | 2CH | Up to 1920×1080@30fps | MAX96705 | 1.5Gbps |
| SG8-BP0102-GMSL2 | 1CH | 2CH | Up to 3840×2160@30fps | MAX9295A | 6Gbps |
| SG8-BP0102-GMSL2F | 1CH | 2CH | Up to 1920×1080@30fps | MAX96717F | 3Gbps |
Getting Started
1. GMSL2 Camera Splitter Integration with Customer's Self-developed Platform
Using the Splitter when connecting to different domain controllers:

Splitter block diagram - Configuration for connecting to different domain controllers
Operating Procedure
- Connect the system as shown in the diagram above.
- Power up the Splitter first.
- Initialize the Controller 1, which will power on and initialize the Splitter-ECU, followed by the Controller 2 power-on sequence and initialize the Splitter-Logger.
- Execute normal operation commands from both Domain Controllers 1 and 2 to bring up the camera.
Operational Logic
- Upon receiving power, the Splitter device automatically configures the connected camera.
- Domain Controller 1 only needs to configure the Splitter as if it were a camera, then trigger it normally to activate the imaging pipeline.
Refer to the software flow and example code below to develop your custom driver implementation.
2. Controller Software Development Example Code
- Driver Development:
/* Example code for MAX9296 I2C initialization */
#define MAX9296_I2C_ADDR 0x90 // 8-bit address
int max9296_init() {
// Initialize I2C bus
i2c_init();
// Disable MIPI output during configuration
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0313, 0x00);
delay_ms(100);
// Configure link settings for GMSL2 (6Gbps)
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0001, 0x02);
// Configure linkA and linkB settings for GMSL2 selection (default value)
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0006, 0xC0);
// Configure MIPI rate to 1200Mbps
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0320, 0x2C);
// Enable MIPI output
i2c_write(MAX9296_I2C_ADDR, 0x0313, 0x02);
return 0;
}
- Splitter Configuration:
/* Example code for Splitter initialization */
#define MAX9295A_I2C_ADDR 0x80 // 8-bit address
int Splitter_init() {
// Initialize deserializer first
max9296_init();
// Reset ISP
i2c_write(MAX9295A_I2C_ADDR, 0x02BE, 0x10); // MFP0 high
// Configure essential registers
i2c_write(MAX9295A_I2C_ADDR, 0x0057, 0x12);
i2c_write(MAX9295A_I2C_ADDR, 0x005B, 0x11);
// Configure datatype to YUV422 8bit
i2c_write(MAX9295A_I2C_ADDR, 0x0318, 0x5E);
// Camera trigger sequence: MFP7 low to high
i2c_write(MAX9295A_I2C_ADDR, 0x02D3, 0x00); // MFP7 low
delay_ms(300);
i2c_write(MAX9295A_I2C_ADDR, 0x02D3, 0x10); // MFP7 high
// Initialize sensor,if without ISP, skip this step
sensor_init();
return 0;
}
int sensor_init() {
// Initialize sensor
i2c_write(sensor_I2C_ADDR, 0x0102, 0x0001);
// Additional sensor initialization parameters
// (Refer to Camera Information documentation for the complete sensor register configuration)
}
Integration Steps
-
BSP Integration:
- Modify the device tree to include the GMSL2 interface configuration
- Add the camera driver to kernel build configuration
- Configure the media controller pipeline for the camera
-
Application Development:
/* Example code for capturing camera frames */
#include "camera_api.h"
int main() {
// Open camera device
int fd = open("/dev/video0", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("Failed to open camera device");
return -1;
}
// Configure video capture format
struct v4l2_format fmt = {0};
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = 1920;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = 1536;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV;
if (ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set format");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
// Request and map buffers
// ... (buffer setup code) ...
// Start streaming
// ... (streaming code) ...
// Capture and process frames
// ... (frame processing code) ...
// Cleanup
close(fd);
return 0;
}
Step 2: Data Processing
After receiving the module data through the GMSL2 interface:
- Data Reception
- GMSL2 protocol implementation
- Data rate configuration
- Image Processing Pipeline
- YUV422 8bit data parsing
- Image format conversion
Technical Support
-
Documentation
- Comprehensive register descriptions
- Integration guides
-
Engineering Support
- Technical consultation
- Debugging assistance
- Performance optimization
SENSING Technology provides expert technical support for integration with most platforms. For detailed documentation, sample code, and technical assistance, please contact our support team.